Muscle Strengthening Activities and Retinopathy
Abstract
Emily Frith, Paul D. Loprinzi
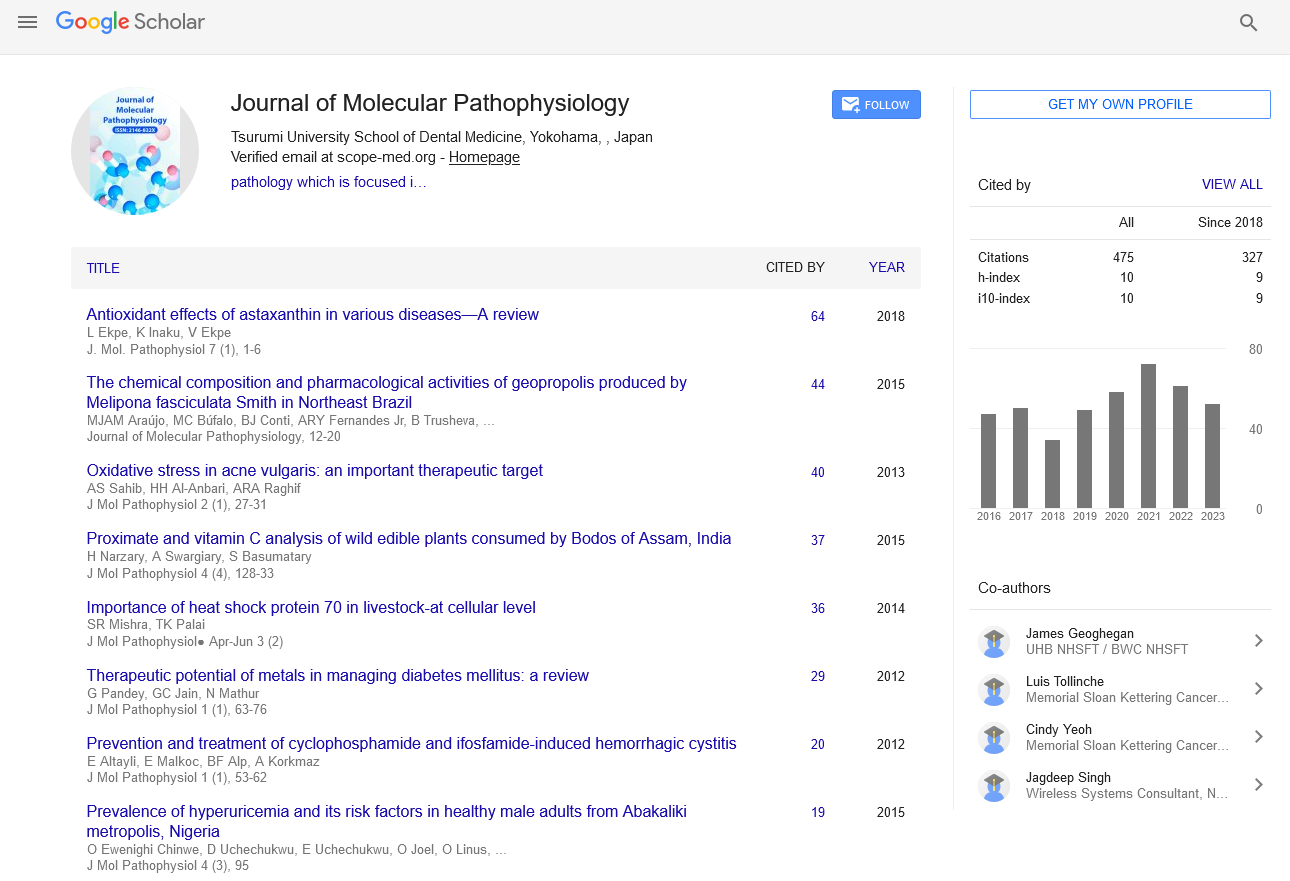
Background: Participation in muscle strengthening activities (MSA) is a neglected health behavior that can have substantive health benefits. Objective: We evaluated the specific association between MSA and retinopathy among a national sample of the broader U.S. adult population, which has yet to be investigated in the literature. Results: Compared to those with no retinopathy, those who engaged in MSA had a 36% (odds ratio [OR] = 0.64; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.49-0.85; P = 0.004) reduced odds of having mild retinopathy. MSA was not statistically significantly associated with reduced odds of moderate-to-severe retinopathy (OR = 0.85; 95% CI = 0.13-5.32; P = 0.85). Conclusion: Promotion of MSA is of major public health interest.
PDF