Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology
The Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology has a target audience of specialists, residents and scientists in physiology, pharmacology, biochemistry, pathology, molecular biology, genetics, epigenetics and other related medicinal fields. The main focus will be the pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment modalities of metabolic disorders such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, metabolic syndrome as well as neurodegenerative disorders.
Submit manuscript at www.scholarscentral.org/submissions/molecular-pathophysiology.html
Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process):
Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology is participating in the Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process (FEE-Review Process) with an additional prepayment of $99 apart from the regular article processing fee. Fast Editorial Execution and Review Process is a special service for the article that enables it to get a faster response in the pre-review stage from the handling editor as well as a review from the reviewer. An author can get a faster response of pre-review maximum in 3 days since submission, and a review process by the reviewer maximum in 5 days, followed by revision/publication in 2 days. If the article gets notified for revision by the handling editor, then it will take another 5 days for external review by the previous reviewer or alternative reviewer.
Acceptance of manuscripts is driven entirely by handling editorial team considerations and independent peer-review, ensuring the highest standards are maintained no matter the route to regular peer-reviewed publication or a fast editorial review process. The handling editor and the article contributor are responsible for adhering to scientific standards. The article FEE-Review process of $99 will not be refunded even if the article is rejected or withdrawn for publication.
The corresponding author or institution/organization is responsible for making the manuscript FEE-Review Process payment. The additional FEE-Review Process payment covers the fast review processing and quick editorial decisions, and regular article publication covers the preparation in various formats for online publication, securing full-text inclusion in a number of permanent archives like HTML, XML, and PDF, and feeding to different indexing agencies.
unique casino - unique casino bonus
2021, Volume 10, Issue 8
Commentary
-
Skin Troubles and Noninvasive Procedural: Dermatopathology
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(8): 1 - 2
Editorial
-
Rhabdomyolysis (Potentially Life-Threatening Syndrome)
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(8): 1 - 1
Editorial
-
Nephrological Disorder (Rare Case): Amyloidosis
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(8): 1 - 1
Commentary
-
Descriptive Details Regarding Pathophysiology of Ulcers
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(8): 1 - 2
Commentary
-
Hormonal Imbalance And Hormone Regulated Issues
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(8): 1 - 2
2021, Volume 10, Issue 12
Commentary
-
Molecular Biology and Immunochemistry to Biochemistry
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(12): 1 - 1
Commentary
-
The Next Paradigm and pharmacology Society Strategic Plan
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(12): 1 - 1
Editorial
-
A Comprehensive Definition and Pathophysiology of Metabolic Syndrome
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(12): 1 - 1
Commentary
-
Epigenetics Beyond the Chromosomal Protein Based Inheritance
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(12): 1 - 1
Editorial
-
Obesity and their Paradoxical Association with Diabetes Mellitus
J Mol Pathophysiol. 2021; 10(12): 1 - 1
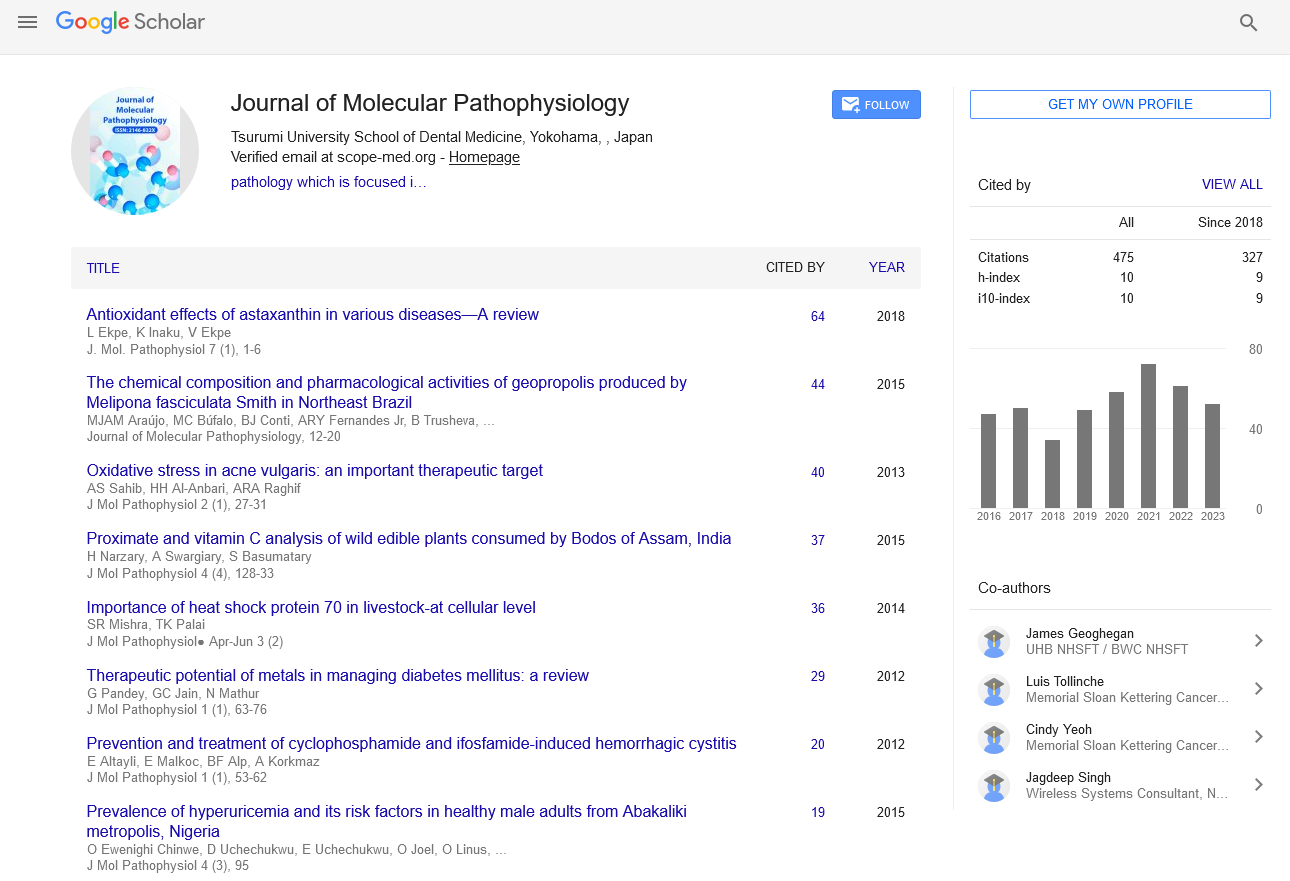
h-index
Articles published in Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology has got h-index 10 , which means every article in Journal of Molecular Pathophysiology has got 10 average citations.